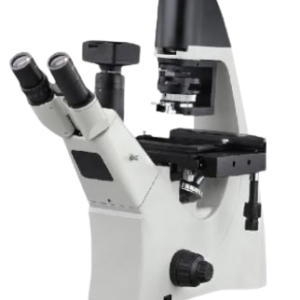
BINOCULAR MICROSCOPE
MAKE DINESH SCIENTIFIC
DESCRIPTION
Because they allow researchers and scientists to examine and examine tissues, cells, and other biological material at a microscopic level, microscopes are essential tools in pathology and medical science. Research and pathology microscopes are made to specifically address the needs of the medical, biological, and allied sciences sectors. The following are some essential elements of using microscopes in research and pathology settings:
LIGHT MICROSCOPES:
- The most popular kind of microscope used in pathology and research are brightfield microscopes. They are useful for seeing stained specimens and offer a bright background.
PHASE-CONTRAST MICROSCOPES:
- When viewing translucent or unstained materials, such living cells, phase-contrast microscopy is especially helpful. It improves these specimens’ contrast without the requirement for staining.
FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPES:
- Research uses fluorescence microscopy extensively. It entails labeling certain molecules or structures within cells with fluorescent dyes or proteins to enable fine-grained imaging of individual cell components.
PATHOLOGY DIGITAL:
- Digital imaging technology is used in the collection, organization, and analysis of pathology data in digital pathology. Pathologists can see and evaluate digital slides using whole-slide imaging, which facilitates remote diagnosis and teamwork.
MECHANIZED MICROSCOPY:
- Microscopy technologies are becoming more and more automated, enabling higher throughput analysis and more productivity in pathology and research labs.
RESEARCH USES:
- In several scientific fields, such as cell biology, microbiology, neuroscience, and developmental biology, microscopes are essential instruments. The structure and operation of cells, tissues, and organisms are studied by researchers using microscopes.
TECHNICAL DETAILS:
| MODEL | DS-BM-100 |
| LED Lifetime | 60,000 hours |
| Focusing | · Stage height movement (Coarse stroke: 15 mm), coarse adjustment limit stopper, torque to prevent damage, fine focus knob (2.5 µm gradations)
· Focus lock to protect objective and specimen. Both-side coarse and fine adjustment knobs. |
| Revolving Nosepiece | Fixed inward-facing quadruple nosepiece |
| Optical System | Infinity corrected optical system for bright field and dark field observation |
| Illumination System | Built-in transmitted illumination system: LED (2-3 watts) with fly-eye or similar technology for eco-uniform illumination |
| Stage | · Reckless mechanical stage with wire movement
· Traveling range: 76 mm (X) x 30 mm (Y), specimen holder, specimen position scale |
| Eyepiece | 10X with field number (FN): 20 (Anti-fungus) |
| Storage Compartment | Located at the back of the microscope for storing the power cable after use |
| Security Feature | Built-in security slot for attachment of an anti-theft cable |
| Optional Capability | Ability to use a reflection mirror for transmitted light |
| Object Marker | The objective/eyepiece micrometer and object marker will be supplied. |
| Observation Tube | 30° inclined binocular tube, interpupillary distance: 48-75 mm, eye points: 370.0 – 432.9 mm, fall-prevention pin to lock eyepiece, left and right diopter |
| Objectives | Plan achromat, anti-fungus objectives:
4X (NA: 0.10, W.D: 27.8 mm) 10X (NA: 0.25, W.D: 8.00 mm) 40X (NA: 0.65, W.D: 0.6 mm) 100X oil (NA: 1.25, W.D: 0.13 mm) |










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.