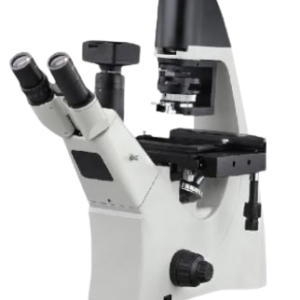
COMPRESSION MOULDING MACHINE
Make Dinesh Scientific
DESCRIPTION
Presses for laboratory compression molding are made to prepare different kinds of product samples.The machine’s four-pillar architecture will provide consistency and rigidity in paralism to maintain the button, slab size, and compaction of various polymer materials and matallic powders.This machine is also employed in the manufacture of samples.The electrical heater types of cartridges have a long lifespan.PID-controlled SSR-type heating control technology guarantees highly accurate platen heating and precise preset heating to guarantee very accurate product quality.Several compression laboratory presses are supplied by the hydraulic systems to various reputable industries for their dependable R&D and laboratory usage. These systems guarantee the set pressure without dropage during the curing cycle (compression cycle).
PREPARING THE MATERIALS:
- RAW MATERIALS: Thermosetting polymers like phenolic, melamine, epoxy, and rubber compounds are frequently utilized in compression molding.
- PRE-FORMS: The material is usually supplied as pre-formed sheets or pellets that have been measured and shaped.
MOLD CREATION:
- A cavity and a core comprise the two halves of the mold.
- With meticulous attention to details like parting lines, gates, and vents, the mold is created to precisely match the specifications of the finished product.
FILLING THE MOLD:
- Either the heated pre-form holder inside the mold or the open mold cavity are used to hold the pre-form material.
- When the mold is closed, the material inside the two parts is brought together.
WARMING:
- After that, heat is applied to the closed mold, softening and pliableizing the material.
- The particular material being utilized determines the temperature and heating time.
CONDENSATION:
- Pressure is then applied to the mold when the material has softened. The material is compressed as a result, being forced to conform to the mold cavity’s shape.
- For thermosetting polymers, the curing process is initiated by the combination of heat and pressure.
REFRIGERATION:
- The mold is cooled to solidify the material and finish the curing process once the material has taken on the shape of the mold.
- To guarantee that the material maintains its final form and qualities, cooling time is essential.
COMPRESSION MOLDING’S BENEFITS:
- Ideal for intricate and sizable components.
- Lower equipment and tooling expenses than with injection molding.
- Excellent for highly viscous compounds.
RESTRICTIONS:
- Cycle times are slower than with injection molding.
- Not as suitable for complicated or thin-walled parts.
- Labor-intensive than some other methods of molding.
TECHNICAL DETAILS:
| MODEL | DS-CM – 40 |
| Capacity | 40 Metric Tons |
| Automation Grade | Fully Automatic |
| Material | Sturdy Steel Structure |
| Stroke | 300 millimeters |
| Power Source | Electrical Power |
| Power Consumption | 3 Kilowatts |
| Surface Treatment | Utilizes Standard Surface Heating Technology |
| Weight | 750 Kilograms |
| Power Source | Electrical Power |












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.